Sporadic Ataxia Lab Investigations
Design Setting and Participants We examined a consecutive series of 76 patients presenting to a tertiary referral center for evaluation of chronic progressive cerebellar ataxia. Routine laboratory investigations as well as serum ceru- loplasmin 232mgl were within normal limits.
Cerebellar Disorders Chapter 19 Uncommon Causes Of Movement Disorders
Twelve individuals 115 with gluten sensitivity underwent duodenal biopsy and extensive clinical electrophysiological neuropsychological radiological and laboratory investigations including human leucocyte antigen HLA typing.

Sporadic ataxia lab investigations. Overview of Adult Onset Cerebellar Ataxia. Adult-onset sporadic ataxia where a genetic cause was clini-cally suspected but genetic screening or sequencing results were negative were labeled as undetermined ataxia. As a consequence a thorough review including age of onset course of disease mode of inheritance detailed clinical evaluation brain imaging and finally focused genetic testing is needed for diagnosis.
Apart from a careful history and clinical examination an MRI is required in all patients. Next-generation sequencing is enabling many more idiopathic ataxias to be given a genetic cause. Sporadic adult-onset ataxia SAOA is a nongenetic neurodegenerative disorder of the cerebellum of unknown cause which manifests with progressive ataxia.
It is important to consider examination findings especially those. Introduction Sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease sCJD includes a broad spectrum of clinicalpathological subtypes which complicates the clinical differential diagnosis with other rapidly progressive neurological syndromes. MRI of the brain may provide a clue to the diagnosis of.
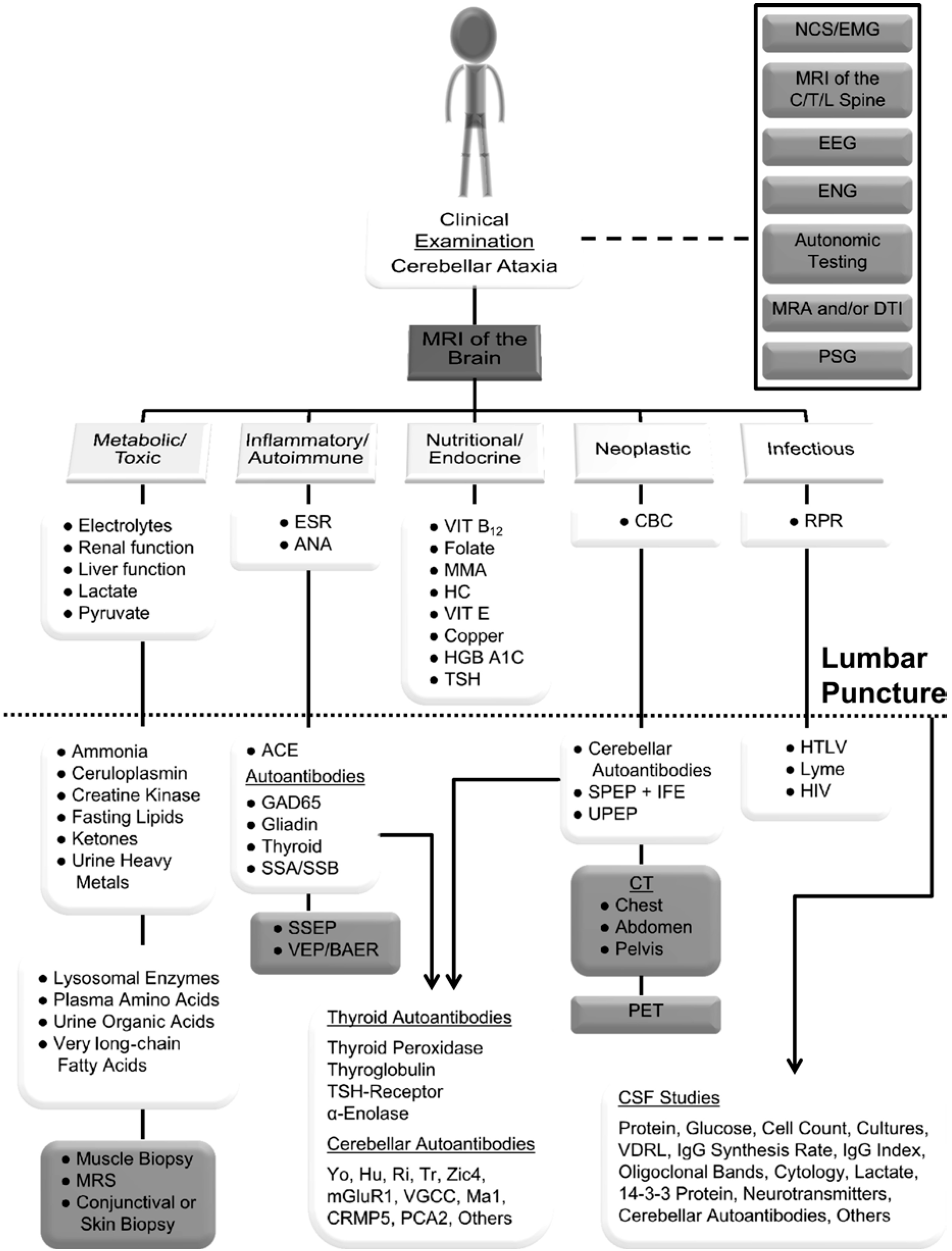
Among the sporadic ataxias in this Japanese cohort 647 had a diagnosis of OPCA and 353 cortical cerebellar atrophy. Unfortunately the frequency of MSA-C cases among individuals with OPCA in this study was not presented. The wide spectrum of possible causes of sporadic adult-onset ataxia requires a rational strategy that allows a correct diagnosis to be made in reasonable time without unnecessarily wasting resources for diagnostic and laboratory tests figure 4 Table 2 Table 3.
The cerebellums main function is to integrate information relayed to it and facilitate the execution of precise movements. The T2 weighted figure 1 and susceptibility weighted figure 2 MR images of the brain showed areas of linear hypointensity along the sylvian fissures cortical sulci surfaces of the brainstem and cerebellum. Recent evidence suggests that ataxia may be the only manifestation of GS and that it may be one of the causes of sporadic ataxia.
The ataxias are clinically heterogenous disorders caused by pathological processes affecting the cerebellum and cerebellar pathways resulting in impaired coordination. The commonest ataxia identified was EA2. Objective To investigate the contribution of genetic disease in a population of patients with predominantly adult- and sporadic-onset cerebellar ataxia.
Twelve individuals 115 with gluten sensitivity underwent duodenal biopsy and. Similar genetic heterogeneity was also noted in 46 patients with sporadic and familial cerebellar ataxia studied with exome sequencing Fogel at al 2014. Aim To provide a better characterisation of clinical features and results of diagnostic investigations especially at an early disease stage in patients with sCJDVV2.
Motor symptoms in HD are typically related to chorea and occasionally parkinsonism myoclonus and dystonia. Owing to the aetiological variability and complexity of the hereditary subtypes adults with late-onset progressive sporadic cerebellar ataxia are a challenging subset of neurological disorders. Using NGS positive results were obtained in 32 of 146 patients tested.
Sporadic late-onset cerebellar ataxias should be exhaustively investigated to identify the underlying causes that are numerous including. A total of 104 patients with sporadic cerebellar ataxia were tested for antigliadin and antiendomysium antibodies. Rapidly progressive ataxia warrants urgent investigation particularly to exclude underlying malignancy.
Sporadic ataxia revealed the presence of an HLA-DQB10201 fi xation instability were accompanied infrequently by saccade slowing double vision and upward gaze palsy. This includes obtaining details such as family history whether the ataxia is acute intermittent or chronic any precipitants and associated conditions. A total of 104 patients with sporadic cerebellar ataxia were tested for antigliadin and antiendomysium antibodies.
The scores are based on patient performance of. A genetic cause was identified in 156 13 of sporadic cases with other causes being alcohol excess 12 and cerebellar variant of multiple system atrophy 11. Serum levels of anti-gliadin anti-transglutaminase 2 TG2 and anti-transglutaminase 6 TG6 antibodies measured in 125 patients with ataxia 100 patients with.
Ataxia in patients with overt lesions detected by imaging can often be asymmetrical. Non-choreiform movements such as. Almost half phenotype in.
Twelve individuals 115 with gluten sensitivity underwent duodenal biopsy and extensive clinical electrophysiological neuropsychological radiological and laboratory investigations including human leucocyte antigen HLA typing. Immunity may be an under-recognised and potentially reversible cause of progressive ataxia. SAOA also needs to be differentiated from multiple system atrophy of cerebe.
Documentation of other nervous system involvement particularly basal ganglia and autonomic dysfunction is critical for the diagnosis of MSA-C in patients with sporadic ataxia Case 9-2. Brain MRI DaT scan genetic analysis and to some extent muscle biopsy thoracic-abdominal-pelvic tomodensitometry and cerebrospinal fluid analysis were the most relevant investigations to explore sporadic late-onset cerebellar ataxia. The sec-ondary cause group included patients who were determined to have acquired causes through intensive investigations.
To describe a unique case of a woman who presented as a progressive cerebellar ataxia with no family history of neurological diseases that after extensive investigation was diagnosed as Huntingtons Disease HD. Investigations of value include an MRI of the brain which excludes structural lesions and documents cerebellar atrophy with or without brain stem or upper spinal cord atrophy. A total of 104 patients with sporadic cerebellar ataxia were tested for antigliadin and antiendomysium antibodies.
Additional prospective screening for Friedreichs. Targeted investigations will then depend on the clinical assessment. Clinical presentation laboratory investigations and exome sequencing results for 35 patients with unexplained ataxia.
It is distinguished from hereditary ataxias and from acquired ataxias. However other studies in Japan and elsewhere confirm that MSA-C is the most common form of sporadic ataxia. For older patients presenting with sporadic degenerative ataxia neurologists should consider the diagnosis of multiple system atrophycerebellar type MSA-C.
To investigate the prevalence of gluten ataxia among patients with ataxia in China. SARA is an 8-item performance based scale yielding a total score of 0 no ataxia to 40 most severe ataxia.

Scheme 1 Differential Diagnosis Of Syndrome Spinocerebellar Ataxia Download Scientific Diagram

Diagnostic Investigations In Adults Download Scientific Diagram