Define Sporadic Alzheimer's Disease
Alzheimers Disease Pathology Originates in the LC A recent theory of sporadic late-onset Alzheimers disease development based on an extensive analysis of. Alzheimers disease AD is a progressive neurodegenerative disease with no cure characterized by extracellular amyloid beta A β plaques intracellular phosphorylated microtubule-associated tau protein p-Tau tangles and age-related memory loss.

Risk Factors Associated With Alzheimer S Disease This Figure Shows Download Scientific Diagram
It occurs primarily in people between the ages of 60 and 70 who have little or no hereditary connection to the disease.

Define sporadic alzheimer's disease. These factors include genetic mutations and environmental and genetic risk factors. Discuss the use of cholinesterase inhibitors. Chapter 7 Atypical and young-onset Alzheimers dementia.
Preclinical Alzheimers disease is defined as biomarker evidence of Alzheimers pathological changes in cognitively healthy individuals. Familial Alzheimers disease is an inherited and uncommon form of AD. In contrast sAD is caused by multiple linked factors that disrupt the balance between Aβ production and Aβ clearance.
Sporadic Alzheimers disease begins as episodes of brain ischemia and ischemically dysregulated Alzheimers disease genes Mol Neurobiol. Describe the three most common forms of atypical Alzheimers disease. Sporadic Alzheimers Disease Most cases of AD are sporadic with dominantly inherited forms accounting for less than 1 of the total.
We observed earlier age of onset of AD to be related positively to longer duration of disease. However mechanistic links between aging and AD pathology remain elusive. Sporadic Alzheimers disease can affect adults at any age but usually occurs after age 65 and is the most common form of Alzheimers disease.
Sporadic Alzheimers Disease AD accounts for the overwhelming majority of all AD cases and exclusively affects people at old age. While this may be reasonable for the amyloid and APOE groups the wider sporadic Alzheimers disease is likely to show more variability in the event sequence due to the inherent disease heterogeneity driven perhaps by genetic eg. Except for the autosomal dominant AD group there was an earlier age of onset in FAD probands.
Whether all etiologic forms of Alzheimers disease AD share a final common pathway is a major issueWe determined the severity and regional distribution of neuronal loss amyloid plaques neuritic plaques NPs and neurofibrillary tangles NFTs and calculated the ratio of neuronal loss to NPs and NFTs in brains of 19 familial AD FAD patients with linkage. The presence or absence of APOE4 Schott et al 2006 or lifestyle factors. Alzheimers disease can be either sporadic or familial.
Chapter 8 Treating Alzheimers disease. Tau is the major component of the intracellular filamentous deposits that define a number of neurodegenerative diseases including the largely sporadic Alzheimers disease progressive supranuclear palsy corticobasal degeneration Picks disease and argyrophilic grain disease as well as the inherited frontotemporal dementia and parkinsonism linked to chromosome 17. This review of Alzheimers disease assembles a variety of findings relevant to the.
Inheritance of the ϵ4 allele of apolipoprotein E APOE is the only well-established genetic risk factor for sporadic. FAD is caused by genetic mutations that drive increased Aβ production. Modelling sporadic Alzheimers disease.
Familiar AD usually strikes earlier in life defined as before the age of 65. Alzheimers disease AD is a neurodegenerative disorder clinically characterized by early memory loss and progressing into dementia. Compare conventional and atypical antipsychotics.
We fractionated frontal cortical grey matter from human Alzheimers disease and control subjects into four biochemically defined pools that represent four distinct compartments. Alzheimers disease and the genes involved in neurofibrillary tangles 5. Familial Alzheimers disease is a very rare genetic condition caused by a mutation in one of several genes.
Patients with subjective cognitive decline have been identified as a useful population in whom to look for preclinical Alzheimers disease. FAD usually implies multiple persons affected in one or more generation. 2-6 The long preclinical phase of AD is an opportunity to identify the changes in pathophysiological.
N Engl J Med 2010. Familial Alzheimers disease can be linked to changes in particular genes but it is rare. Of the two main forms of Alzheimers Sporadic Alzheimers Disease is the more prevalent.
FAD and sporadic Alzheimers disease SAD cases did not differ in clinical features incidence of risk factors for dementia or MRI or PET features. A majority of cases manifest as a late onset sporadic form but genetically the disease is divided into familial cases and sporadic cases. Most forms of Alzheimers disease AD are sporadic sAD or inherited in a non-Mendelian fashion and less than 1 of cases are autosomal-dominant.
Alzheimers disease can strike adults of either sex. Alzheimers disease AD is an neurodegenerative disease and the most common cause of dementia. ABSTRACT Alzheimers disease AD is an age-related progressive neurodegenerative disorder.
The single sequence the EBM identifies maximizes. The vast majority of cases of Alzheimers disease are not caused by known changes to specific genes this type is called sporadic Alzheimers disease. It usually occurs in old age.
Solublecytosolic peripheral membranevesicular cargo integral lipidmembranous pools and aggregatedinsoluble debris. State the role of acetylcholine. And Frank M.
Forms of sAD do not exhibit familial. As opposed to Early Onset Alzheimers which researchers have shown to be passed down directly from one generation to another through the occurrence of a. 1 It has been documented that amyloid beta Aβ deposition tau pathology and neuronal degeneration precede clinical symptoms.

Comparison Of Autosomal Dominant Alzheimer S Disease With Sporadic Download Table
Alzheimer S Disease Definition Causes Diagnosis Treatment
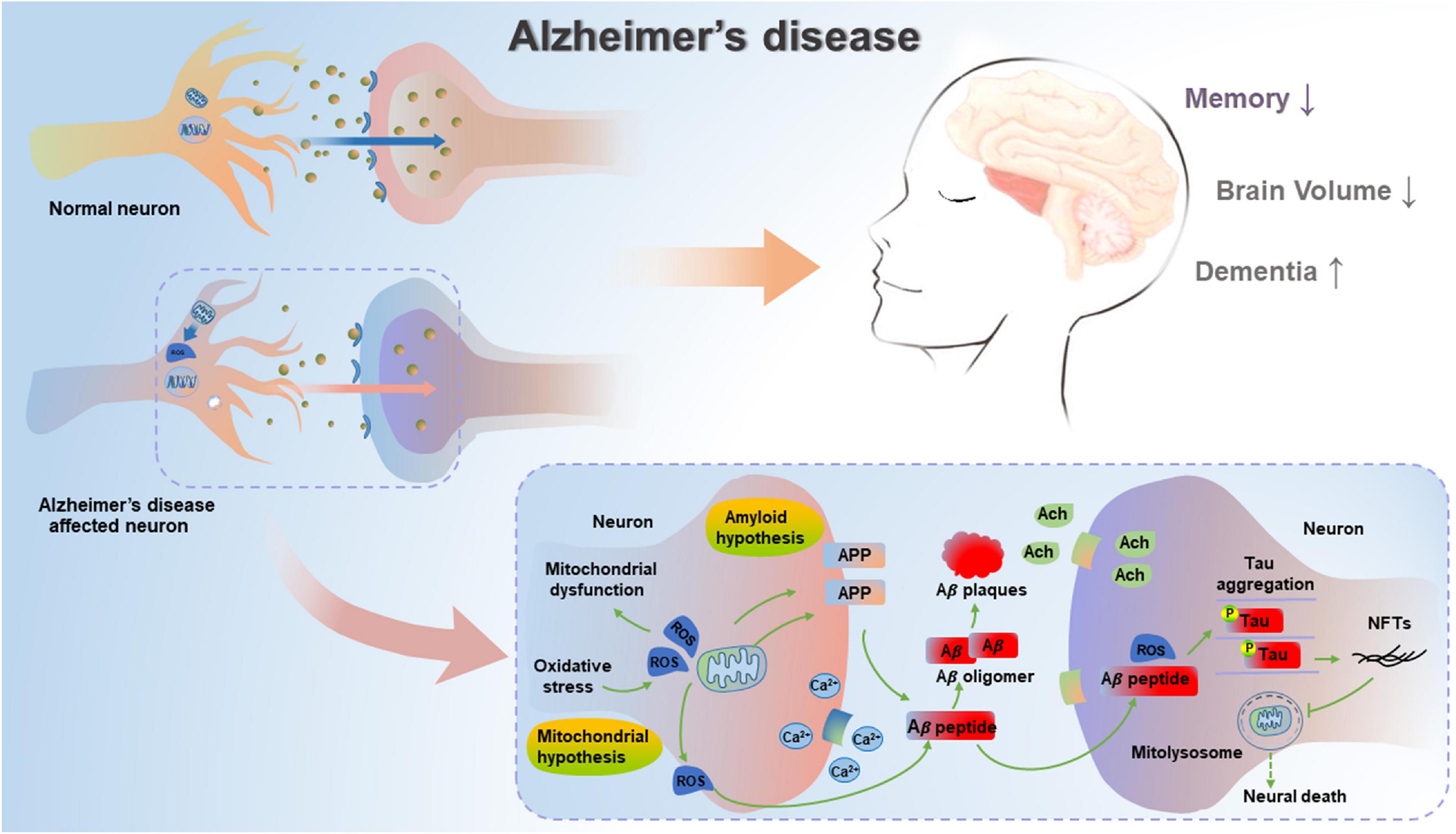
Frontiers Exercise Induced Benefits For Alzheimer S Disease By Stimulating Mitophagy And Improving Mitochondrial Function Aging Neuroscience