Sporadic Vs Hereditary Cancer
The only difference is that the first mutation is inherited and the second is somatic in familial cancer whereas in sporadic cancer both mutations are somatic. They dont mean that a person will absolutely have that cancer.
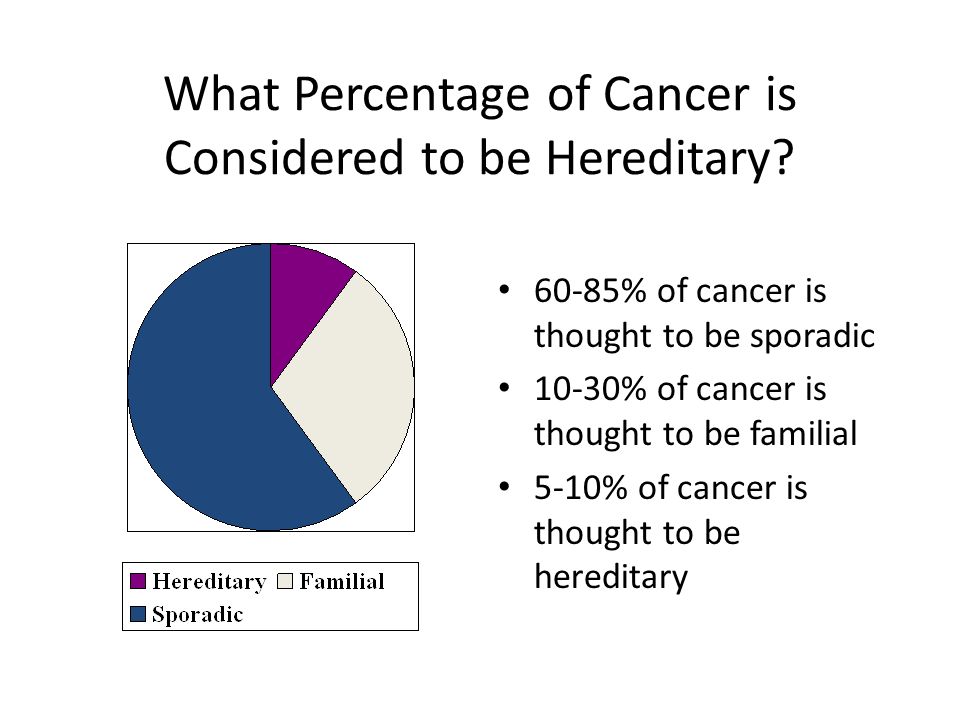
What Percentage Of Cancer Is Considered To Be Hereditary Ppt Video Online Download
Its important to remember that these types of inherited mutations only increase the likelihood that a person will develop cancer in most cases.

Sporadic vs hereditary cancer. Signs suggesting hereditary cancer include. These genes are sometimes referred to as DNA damage repair or DDR genes. Inherited Cancer is caused.
However in most sporadic cancers an unknown number of factors which are. Help your patients take action for their health. But even in this situation even if we call this hereditary cancer in fact there is always contribution to some kind of environmental factors in the development of cancer in this particular populations.
In contrast to hereditary cancers with a single genetic factor of high penetrance the reason why sporadic cancer develops seems to be multifold. By germline mutations any detectable and heritable variation in the lineage of germ cells in suppressor genes. Other Pages You Might Like.
Many families however find themselves caught at the boundary between these two entities. DNA damage repair genes. In a minority of sporadic cancers a single etiologic factor can be identified.
Differences in clinical characteristics and survival between hereditary ovarian cancer patients and sporadic cases are difficult to explain. They may be caused by differences in the molecular pathway of carcinogenesis of hereditary and sporadic ovarian cancer. Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer Lynch syndrome or HNPCC an autosomal dominant disorder is a disease in families where multiple members have colorectal and other forms of cancer.
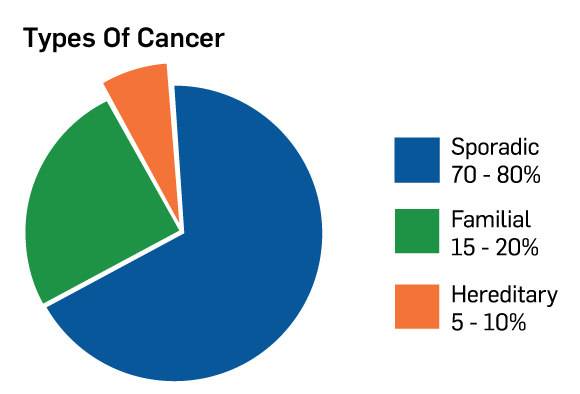
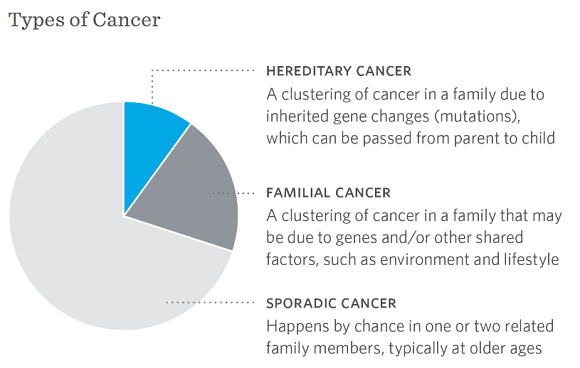
Cancers in people who do have an inherited mutation are called hereditary cancers. The only difference is that the first mutation is inherited and the second is somatic in familial cancer whereas in sporadic cancer both mutations are somatic. Sporadic cancers are believed to arise from gene damage acquired from environmental exposures dietary.
Signs of Sporadic Cancer. Furthermore hereditary breast cancer is associated with a poorer survival and hereditary ovarian cancer with a better survival 4 than their sporadic counterparts which may have consequences for treatment. The contribution of genetic mutations is best regarded as a continuum.
Genes are the instructions that tell. You just need awareness of what triggers the mutation and the discipline to avoid them. Other blood relatives may share these same gene changes.
Later ages of onset 60s-70s Little or no family history of cancer. Surprisingly the p53 genes that create cell abnormalities in hereditary cancer are often the same genes found in sporadic cancers. Sporadic colorectal cancer is the term given to those patients who are affected with the disease but have no family history of this condition.
There are several clues which suggest that there is hereditary cancer in a family. PsiGenex gives you more hereditary cancer panels with more gene coverage to help arm your patients with knowledge. Thus the proportion of hereditary PCCPGLs may exceed estimates of 30 to 40 rendering PCCPGL one of the most inherited tumor entities in existence.
These cancers are referred to as sporadic. Findings of other patients with a clinical presentation of PCCPGL that includes a positive family history early age of presentation and bilateral adrenal or multiple tumors but without known mutations has suggested the presence of. In familial breast cancer genetic abnormalities play a minor role in the risk of breast cancer whereas in hereditary forms BRCA1 BRCA2 and BRCA3 mutations have a significant impact.
However it should be noted that p53 mutations are the most common mutations in sporadic cancers too. Nevertheless only some 5-10 of all cancers are due to germ-line mutations which are generally called inherited cancer for simplification purpose most are autosomal dominant and the vast majority of cancer-associated mutations in these genes occur de novo in somatic cells which are called generally. Sporadic cancer and hereditary cancer differ in several ways that may affect health care decisions.
The rare Li Fraumeni Syndrome illustrates the difference between familial and sporadic cancers. At much younger-than-expected age. Some well-known hereditary cancers include BRCA gene-related breast cancers and colon cancers such as hereditary non-polyposis colon cancer and familial adenomatous polyposis.
Mutation is used in a broad sense and refers to either a point mutation at a specific locus or the loss of a. According to this model both cancers involve the same genomic change in homologous chromosomes. Divergence of the methylator pathway into MSI-L and MSI-H is at least partly determined by the respective silencing of MGMT and hMLH1.
Cancers caused by sporadic variants typically appear later in life and with little or no family history. Mutations in these genes are important in tumour occurrence and pathogenesis. All the cells in our bodies contain thousands of pairs of genes.
We call hereditary cancers a very particular situations where the genetic background of the individuals it then the major risk factor for him or for her. Hereditary cancer often occur earlier than the sporadic form of the same cancer so experts often recommend different screening at a younger age for people with hereditary cancer in their family. Prevention is very doable in sporadic kinds of cancer.
The majority of cancers develop sporadically. It is the way the cancers occur in the family that indicates whether they may be hereditary. Triggers and multiple gene changes over time.
Inherited Cancer is usually diagnosed. Two or more relatives with the same type of cancer on the same side of the family several generations affected. Inherited not the actual cancer.
Age of diagnosis is usually younger than in sporadic forms of cancer often younger than age 50. Hereditary cancers generally are not significantly different from non-hereditary cancers. The majority of cancer-causing variants are sporadic meaning that they occur randomly as a result of age and environmental exposures.
Inherited Cancer risks are. Hereditary cancers are caused in part by gene mutations passed on from parents to their children. People born with cancer related gene mutations have a greater likelihood of developing cancer than the general population.
Cancers in people who do not have an inherited mutation are called sporadic cancers. Certain genes are important for repairing DNA damage. However about 5-10 of cancers are caused by a specific inherited genetic change mutation.
Screening for BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations is difficult. An observable autosomal dominant pattern win a family. Cancer is more likely to develop in more than one site in the body.
These cancers are referred to as hereditary cancer syndrome. Clarity is achieved when cancers showing DNA microsatellite instability MSI are distinguished as sporadic MSI-low MSI-L sporadic MSI-high MSI-H and hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer HNPCC. In Li Fraumeni syndrome there is an inherited mutation in the p53 gene and a variety of cancers arise in persons with this mutation.
Multiple family members have the same or related types of cancer.
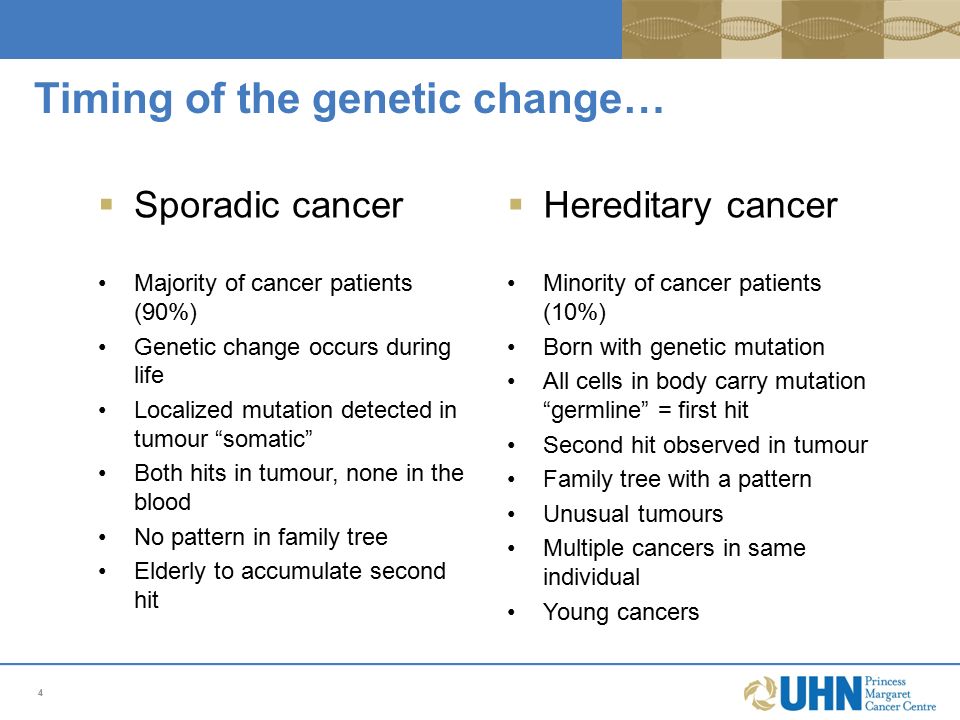
Hereditary Cancer The Next Generation Ppt Video Online Download