Sporadic E Forecast
Keen sporadic-E watchers will monitor the 10 metre band taking note of the locations of. The links below provide information about Sporadic-E and Spread-F.
As the name indicates sporadic E is not easy to predict.
Sporadic e forecast. Predict sporadic E layer cloud formation. Fig2 sporadic E foEs temporal analysis. Send formated DX spots indicating clearly both locators and the type or propagation.
Sporadic E or Es is a mode of radio propagation that occurs on occasions. Please note the RSGB is not responsible for the content of external websites. The rest of information is useless and it doesnt interest anybody.
The Japanese Space Weather Forecast Center for example has reported preliminary results in predicting sporadic E clouds a few days ahead of its formation 1. These are a rough guide and do not take into account long-path openings or sporadic E short-path openings in May-August. Hourly update based on ionosonde data of Jeju and Icheon.
Do not chat in the DX-Cluster. This condition affect the long distance radio broadcasting and the wireless emergency alerts. October 18 2015 Foliage Looking Southwest from Lower Front Deck.
Fig1 sporadic E foEs temporal analysis. They can become denser than the normal E layer or even the peak F layer. The large electron density structures and their strong vertical density gradients may seriously affect the radio propagation and navigation systems 1.
If you are a 10 metre band enthusiast you might get it four days in a row mind you not necessarily all day. Maps of July 23. Sporadic-e Propagation at VHF.
Visualization of intensity according to critical frequency. Propagation maps created with HamCAP and based on the predicted smooth sunspot number for the month and CW100w to a dipole at 35ft. LIGHTNING ACTIVITY- Sometimes appears to correlate with Es and often NOT.
A sporadic E layer has significant influence on radio communications and broadcasting and predicting the occurrence of sporadic E layers is one of the most important issues in space weather forecast. It occurs on an occasional basis and can affect radio communication on frequencies from a few MHz up to those much higher than would normally be. A sporadic E layer has significant influence on radio communications and broadcasting and predicting the occurrence of sporadic E layers is one of the most important issues in space weather forecast.
Now you can also receive customized propagation alerts by E-Mail. Live Sporadic-E Map Europe and Transatlantic 30MHzfrom G7IZU. A sporadic E layer has significant influence on radio communications and broadcasting and predicting the occurrence of sporadic E layers is one of the most important issues in space weather forecast.
On 6m you might get parts of four days too perhaps at the peak of activity during the two weeks around the Solstice at the end of June. Orange lines 70 MHz. Coloured lines indicate sporadic-E propagation reported in the following frequency bands during the last 30 minute period.
144 MHz Sporadic-E QSO animated maps in Europe. Investigations in last years showed a high. Map of July 30 1245 - 1400.
November 2015 Same shot a month later with front yard cleaned up. Maps of July 25. While sporadic E layer occurrence and the magnitude of the critical sporadic E frequency foEs have clear seasonal variations significant day-to-day.
Sporadic E also known as Es ie. Issuing alarm for sporadic-E occurrence causing VHF communication failure. Forecasting E-Sporadic ES New point of views falling from the space on E-Sporadic events By Flavio Egano IK3XTV and Tony de Longhi IZ3ESV Abstract There is strong evidence that the E-Sporadic layer at the tempered latitudes should origin from events occurring outside the Earth.
The sporadic E-layer Es appears at an altitude that may vary anywhere between 80 and 120 km. It can affect frequencies normally affected by ionospheric propagation but as the levels of ionisation can rise very high it can affect frequencies much higher than would be expected by normal E region ionisation. It is still not known how this layer actually develops but it can appear at any time of the day with a preference for the late morning and early evening mostly during the summer months and briefly at midwinter with the peak occurring in the early summer.
Blue lines 28 MHz Yellow lines 50 MHz Orange lines 70 MHz Red lines 144 MHz No-lines visible No propagation reported White parallel lines crossing the map daynight terminator Yellow star Sub-solar point. Make sure your locator is OK in the callbook. Map of July 27 1545 - 1630.
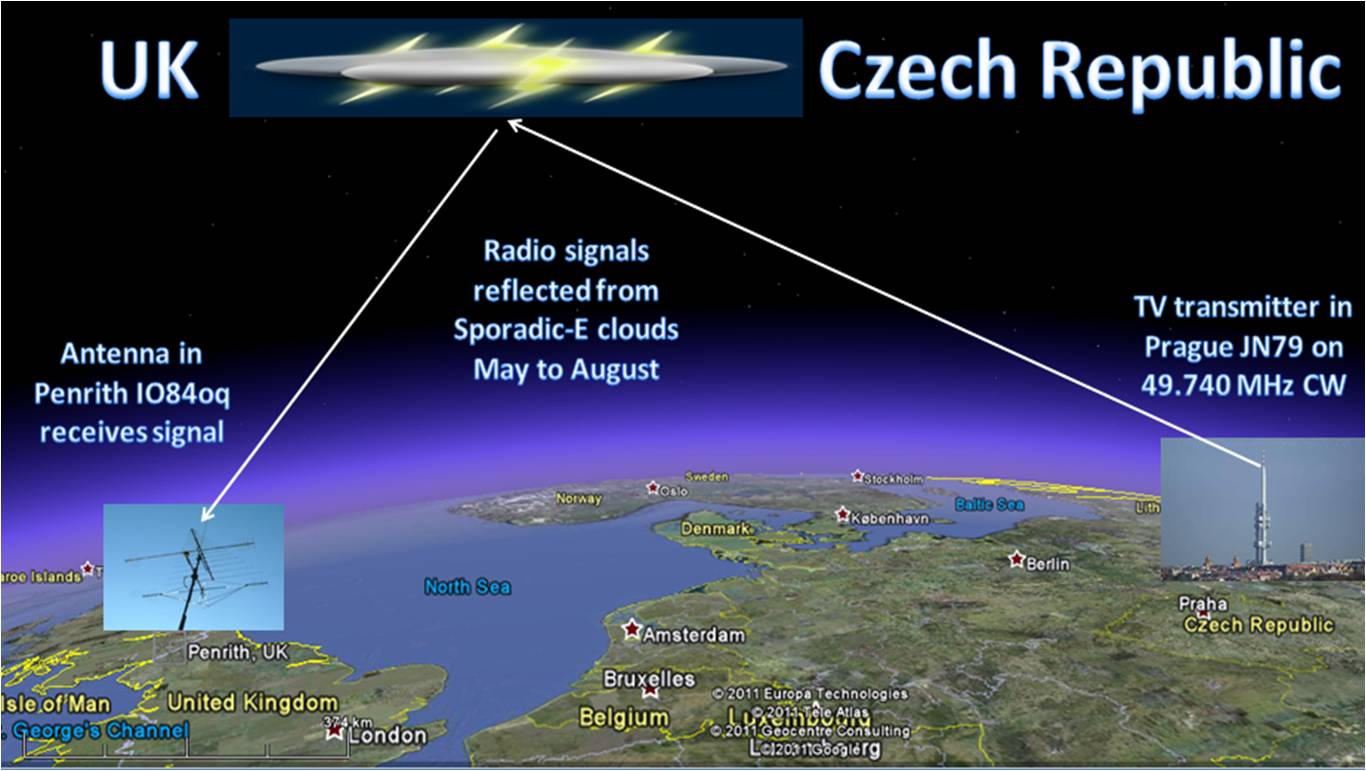
Red lines 144 MHz. Yellow lines 50 MHz. On HF where refraction of signals by higher layers of the ionosphere cause longer distance propagation sporadic-E type conditions are often referred to as short skip.
Coloured lines indicate sporadic-E propagation reported in the following frequency bands during the last 15 minute period. Furthermore when the sporadic- E Es layer develops radio waves at 10 MHz order which normally penetrate the ionosphere will be reflected at the Es layer and propagate anomalously beyond the line of sight. New Hampshire Foliage Tracker.
The maximum useable frequency of a sporadic E s layer MUF_E_s is about 5319 times the depicted critical frequency f_oE_s Source. Obviously Sporadic E is something you cannot count on. Blue lines 28 MHz.
Plot updated every 15 minutes of the critical frequency f oEs of the sporadic E s layer in the vicinity of where your IP address is thought to be located. However while accurate forecasting of local sporadic E clouds is highly desirable it is still elusive. A sporadic E layer has significant influence on radio communications and broadcasting and predicting the occurrence of sporadic E layers is one of the most important issues in space weather forecast.
144MHz sporadic-E from 2001. K1SIXs 6M SPORADIC E INFORMATION PAGE. Based on CW100W to a dipole at 35ft.
Sporadic E Explained - Sporadic E is a form of propagation that can arise with little warning and enable radio frequencies of 150 MHz and more to travel over distances of a. The distance between the transmitter and the receiver of the refracted signal is called the skip distance. You can help generate this page.
This application is available to licenced radio amateurs to produce their own propagation maps. William Hepburns Worldwide Tropospheric Ducting Forecast Site. E sporadic is a form of E layer ionisation that occurs randomly in the ionosphere.
While sporadic E layer occurrence and the magnitude of the critical sporadic E frequency foEs have clear seasonal variations significant day-to-day. Short-Path Propagation from UK. Sporadic E Es layers are thin-layered structures with intense high electron densities at 80120 km altitudes.
Numerical Prediction Of Sporadic E Layer Occurrence Using Gaia Earth Planets And Space X Mol

A Statistical Study Of Anomalous Vhf Propagation Due To The Sporadic E Layer In The Air Navigation Band Sakai 2019 Radio Science Wiley Online Library
E Skip Tropospheric Ducting And Other Vhf Propagation Phenomena Engineering Radio