Sporadic Juvenile Polyp
2 Endoscopically they. This finding suggests that at least in adults even the sporadic JPs might carry an inherent potential for malignancy which has so far only been pointed out for syndromic lesions.
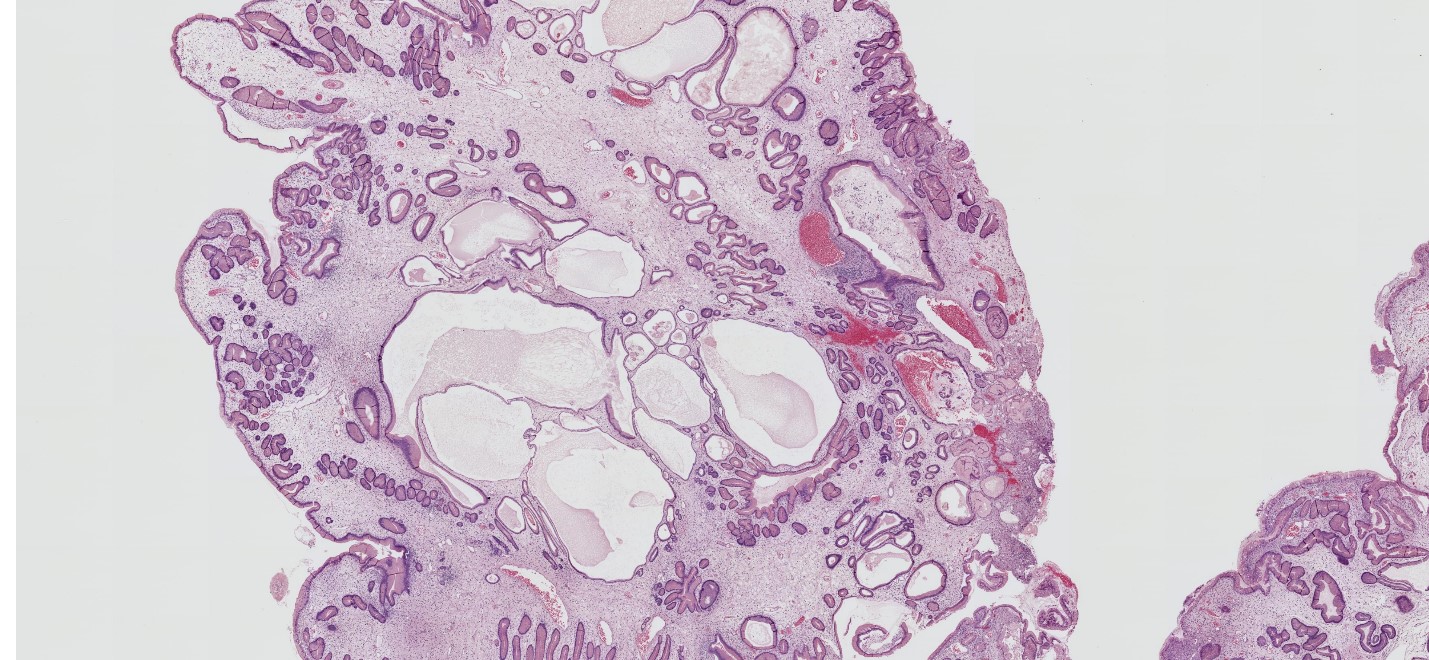
Pathology Outlines Juvenile Retention Polyp
Reactive Inflammatory Polyp.

Sporadic juvenile polyp. More common in inflammatory bowel disease and diverticulitis but may be sporadic. In the sporadic form juvenile polyps have their peak prevalence in children aged between 1 and 7 years. There is some evidence that juvenile polyps can regress but they are certainly seen in adults.
Prominent cystically dilated glands. Juvenile polyposis syndrome. Sporadic Juvenile Polyp.
Most commonly associated with rectal bleeding juvenile polyps usually present as solitary clusters in the rectum itself. A total of 213 patients met the criteria. Common in children without other GI disease.
Endoscopic characteristics of these polyps were indistinguishable from adenomas. Juvenile polyposis is a syndrome presented with multiple. Solitary juvenile polyps.
These polyps may be sporadic or associated with juvenile polyposis syndrome JPS which is an autosomal dominant syndrome with high penetrance linked to abnormalities in the signaling of transforming growth factor-β TGF-B via genetic abnormality of SMAD4 or BMPR1AI genes in about 50 to 60 of patients with JPS. Histologically the lesion was consistent with juvenile polyp JP but showing a few dysplastic glands and a focus of intramucosal adenocarcinoma. Juvenile polyps most frequently are diagnosed before the age of 10 years with the peak age of diagnosis between 2 and 5 years of age.
Adenomatous Change In A Solitary Juvenile Polyp. These can be either sporadic in nature or are associated with various polyposis syndromes such as Peutz-Jeghers syndrome juvenile polyposis syndrome and Cowden syndrome PTEN or multiple hamartoma syndrome as discussed below. For those patients a total of 326 colonoscopy procedures and 435 polypectomies were performed.
Prominent cystically dilated glands. May have irregular dilation but not typically prominent and regular. Common in children without other GI disease.
Sporadic juvenile polyps are thought to be low risk and less likely to have recurrence. Reactive Inflammatory Polyp. Unlike Peutz-Jeghers polyps juvenile polyps may develop sporadically or in association with one of several polyposis syndromes including juvenile polyposis syndrome Cowden syndrome and Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome as discussed in the next section.
Sporadic colonic juvenile polyps are uncommon in adults. Two of these polyps occurred in the caecum which is an uncommon localisation. Juvenile polyps are regarded as hamartomatous polyps and occur in sporadic and familial syndromic settings.
There is increased risk of gastrointestinal neoplasia in patients with juvenile polyposis syndrome but the molecular mechanisms are not known. We report three cases for which clinical manifestations were presence of occult blood in the stool rectal bleeding or chronic diarrhea. Juvenile polyps can occur in a sporadic form or can be part of juvenile polyposis syndrome.
Polyp Inflammatory Myoglandular Polyp Juvenile Polyps and Juvenile Polyposis PeutzJeghers Syndrome Cowden Syndrome CronkhiteCanada Syndrome Hyperplastic and Serrated Polyps Conventional Adenoma Adenomatous Polyposis Syndromes Adenomas and AdenomaLike Dysplasia Associated Lesions or Masses in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. There is possible malignant potential even in nonsyndromic juvenile polyps including solitary polyps. Sporadic juvenile polyps are lesions with potential for neoplastic and even malignant transformation.
Patients with a juvenile polyp should have their large bowel examined by colonoscopy to ensure that they do not have juvenile polyposis. Juvenile polyps are regarded as hamartomatous polyps and occur in sporadic and familial syndromic settings. 1 Their etiology remains unknown.
More common in inflammatory bowel disease and diverticulitis but may be sporadic. Examples include Peutz-Jeghers polyps and juvenile polyps as well as hamartomatous polyps without specific names. In contrast patients with JPS who range from 9 to 50.
They can certainly be seen in adults. In the sporadic form juvenile polyps have their peak prevalence in children between 1 and 7 years of age. Polyps appear similar to sporadic solitary juvenile polyps although syndromic polyps often have a frond-like growth pattern with less stroma fewer dilated glands and more proliferative smaller glands JPS polyps frequently show neoplastic changes to the epithelium not common in sporadic solitary juvenile polyps.
Patients from birth through age 18 with sporadic juvenile polyps or nonsyndromic polyps no family history of juvenile polyposis syndrome and no juvenile polyps proximal from the colon were included. Sporadic juvenile polyps are thought to not harbor any malignant potential. In the absente of a family.
Patients with juvenile polyposis sporadic pol- yps appear to carry no increased risk of malignancy. In addition polyps in juvenile polyposis syndrome frequently show neoplastic changes to the epithelium not found in sporadic. There is a condition known as juvenile polyposis syndrome.
Not a marker for subsequent malignancy. Juvenile polyps are hamartomatous polyps that are identified before an individual is 20 years old. May have irregular dilation but not typically prominent and regular.
In essence juvenile polyps in juvenile polyposis syndrome appear similar to sporadic solitary juvenile polyps although syndromic polyps often have a frond-like growth pattern with fewer stroma fewer dilated glands and more proliferative smaller glands. Juvenile polyps can occur in a sporadic form or be part of juvenile polyposis syndrome. Sporadic juvenile polyps of the colon are considered benign and occur in up to 2 of children under the age of 10 years 8.
Some evidence indicates that juvenile polyps once formed can regress. Most of them are solitary and do not require further follow-up 9.

A Single Crypt Adenoma In Fap B Typical Juvenile Polyp With Erosion Download Scientific Diagram
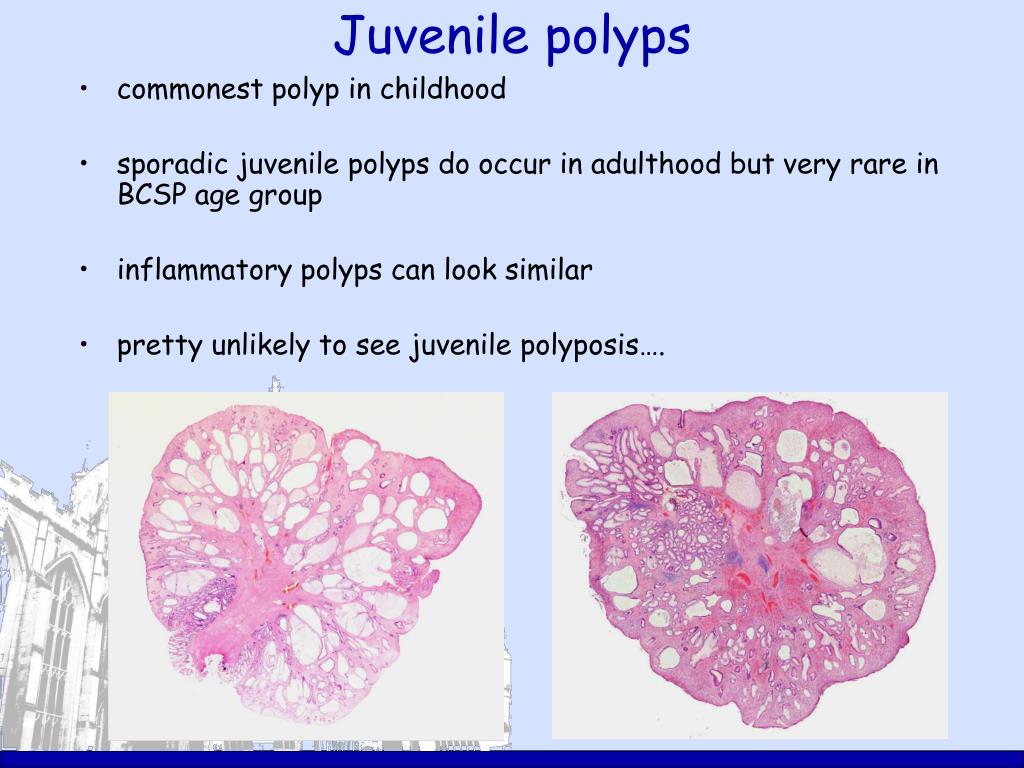
Ppt Special Polyp Types Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 364945
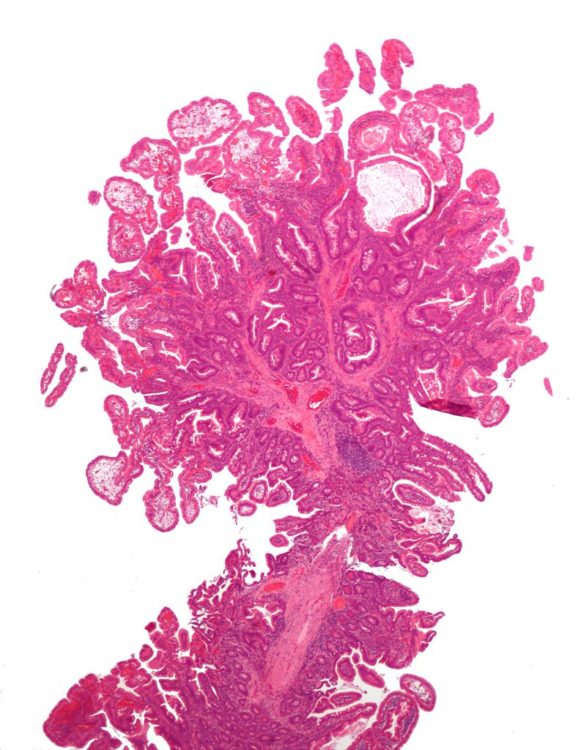
Peutz Jegher S Syndrome Juvenile Polyposis And Hnpcc Lecturio