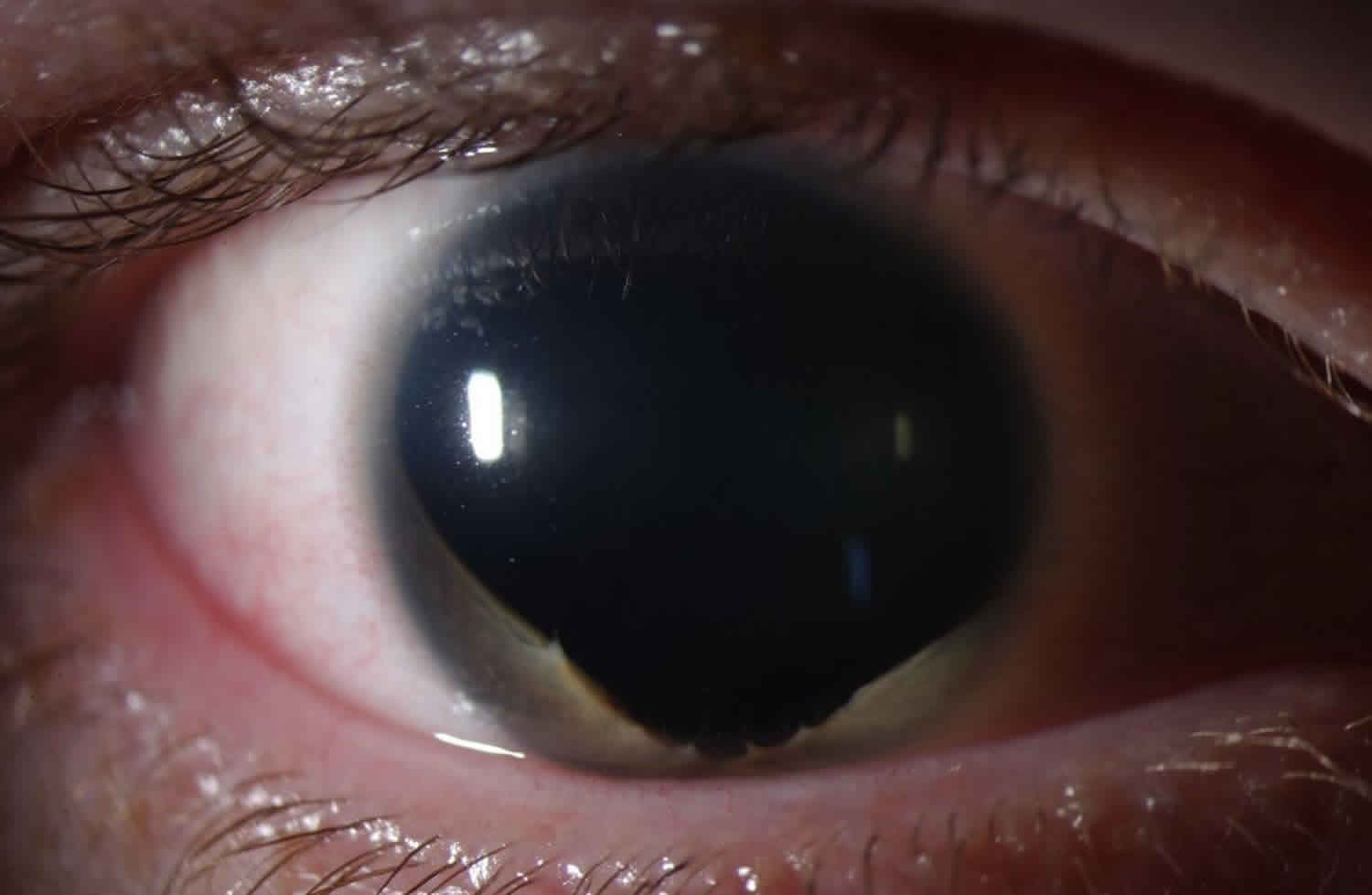
Sporadic And Familial Aniridia
1995 found 4 different mutations in PAX6 in 1 sporadic and 5 familial cases of aniridia. It exists in both sporadic and familial form.

Aniridia American Association For Pediatric Ophthalmology And Strabismus
Elsas FJ Maumenee IH Kenyon KR Yoder F.
Sporadic and familial aniridia. Paired box mutations in familial and sporadic aniridia predicts truncated aniridia proteins. Once a sporadic case is identified a familial inheritance pattern autosomal dominant will occur from then on. A Aniridia Familial 6 PD 590 7-bp Insertion TAAACCG c590ins7 TAA stop B Aniridia Sporadic 7 LNK 790 4-bp Deletion ATGA c790del4 Frameshift3TAA stop C Aniridia Familial 8 LNK 969 C3T c969C3T R203X D Aniridia Familial 8 LNK 969 C3T c969C3T R203X E Aniridia Familial Not detected F Peters anomaly Sporadic Not detected.
The mean age was 254 184 years with 65 sporadic and 35 familial cases and 24 with WAGR Wilms tumor aniridia genitourinary anomalies and mental retardation syndrome. In genetics it is known as an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern. They were examined because they had either isolated sporadic or familial aniridia or aniridia with one or more of the WAGR Wilms tumour aniridia genital anomalies and mental retardation.
This is known as familial aniridia. The mutations are scattered throughout the gene and the vast majority of those reported so far are nonsense mutations frameshift mutations or splicing errors that are predicted to cause premature truncation of the PAX6 protein causing. Aniridia is a rare bilateral congenital malformation of iris due to neuro-ectodermal developmental defect secondary to a mutation in PAX6 gene located on chromosome 11p13.
This is known as sporadic aniridia. It may occur in isolation or associated with. Progressive changes in the angle in congenital aniridia with development of glaucoma.
The paired box mutations that we detected were in both familial three and sporadic two cases. Such deletions may manifest as Wilms tumour-aniridia. A mutation of the PAX6 gene causes malformation of tissue structure in the front part of the eye including iris tissue and results in aniridia.
Both sporadic cases and familial cases with an autosomal dominant inheritance exist. A previously reported mutation and 3 novel ones. Two-thirds of all aniridia children have affected parents.
19 were sporadic and 11 were familial cases. Aniridia can be sporadic or familial. A parent with aniridia can pass on the faulty gene when he or she also has aniridia.
Jastaneiah S Al-Rajhi AA. Of the 13 cases with aniridia and other malformations 5 38 had a chromosomal rearrangement or deletion. In a family with an affected 32-year-old woman and a 10-year-old daughter the mother had bilateral erosion of the cornea and blood vessels on the corneas with bilateral cataracts and also had very thin irides see 6071080008.
This study aims to detect the mutational spectrum of PAX6 and associated phenotypes in southern Indian patients with sporadic and familial aniridia. Newborns with sporadic aniridia are at greatly increased risk of the paediatric nephroblastoma Wilms tumour if they have a deletion encompassing PAX6 and the nearby Wilms tumour predisposition gene WT1 gene. It is said that sporadic aniridia is associated with Wilms tumor in up to one-third of cases.
The frequency of cryptic deletions in familial aniridia was 27 and in sporadic isolated aniridia was 22. This study aims to detect the mutational spectrum of PAX6 and associated phenotypes in southern Indian patients with sporadic and familial aniridia. The familial form is autosomal dominant with complete penetrance but variable expressivity.
Sporadic aniridia refers to cases where a genetic mutation happens at random and a baby is born with aniridia when there is no family history. In this report we describe five new mutations in the paired box region of the human PAX6 gene that are associated with aniridia. Aniridia occurs due to decreased dosage of the PAX6 gene and exists in both sporadic and familial forms.
Aniridia occurs either as an isolated ocular abnormality without obvious systemic involvement or. OSTIGOV Journal Article. Familial aniridia with preserved ocular function.
Note that the FAT5signal is present on both the. The PAX6 gene is responsible for the normal development of the anterior part of the human eye. Mutations in the PAX6 gene have been shown to be the genetic cause of the disease.
Heterozygous null mutations in paired box gene 6 PAX6 are the major cause of the classic aniridia phenotype. Genomic DNA was isolated from peripheral blood. Grant WM Walton DS.
Sporadic cases which means neither parent has Aniridia syndrome is more common. A fault in the gene can arise randomly when neither parent has the condition. There are two ways in which aniridia can be inherited from a parent.
Some of the sporadic cases are caused by large chromosomal deleti. Genomic DNA was isolated from peripheral blood from all participants. A person may be described as having either sporadic aniridia or familial aniridia.
The 11 centromeres are directly labelled withfluorogreen andthe 7centromeres withfluorored. The age range of the patients. Aniridia can be familial or sporadic.
The remainders are sporadic. The 11p13specific cosmidsignal wasdetected using a single layer ofTRITCconjugated anti- digoxigen Boehringer. About two-thirds of cases are familiar with dominant inheritance.
Familial aniridia refers to cases where a baby is born with aniridia which has been inherited from a parent who also has aniridia. Aniridia is a severe eye disease characterized by iris hypoplasia. A total of 49 members from 30 families were clinically diagnosed with the aniridia phenotype of whom 39 patients had total aniridia no visible iris while ten patients presented with partial aniridia loss of some portion of the iris.
Familial inheritance cases mean that one of the childs parents has Aniridia syndrome. Familial aniridia cases show autosomal dominant inheritance with high penetrance but considerable phenotypic heterogeneity. The incidence of aniridia is estimated to be 1 in 60000-100000 live births.
All five mutations predict truncated PAX6 proteins. Of the 14 cases referred with WAGR syndrome 10 71 had chromosomal deletions 2 cryptic and 8 visible. FISHstudies in apatient with sporadic aniridia andt711q312p13 Figure 2 a Results ofin situ hybridisation with the PAX6cosmid FAT5.
Ocular abnormalities included nystagmus 83 cataract 71 dry eye 53 glaucoma 46 keratopathy 45 foveal hypoplasia 41 strabismus 31 and.
Diagnosis And Management Of Aniridia American Academy Of Ophthalmology
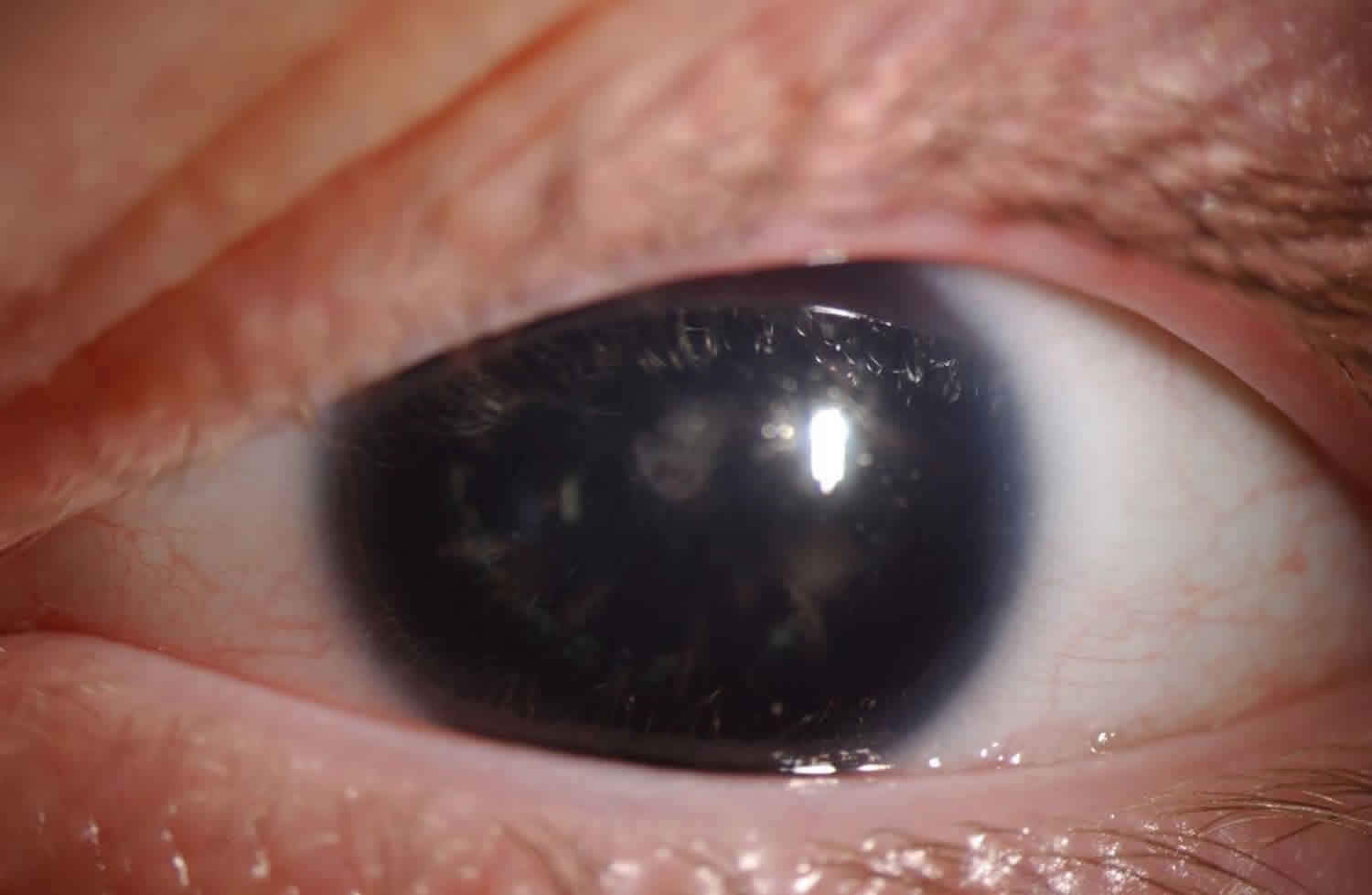
Aniridia Definition Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Prognosis Treatment

Aniridia Showing Absence Of Iris And Peripheral Pannus Eye Of Download Scientific Diagram