Sporadic Als Mutation
The age of onset is earlier by 5 years on average in this population but the penetrance is not complete until after 80 years explaining the cases of pace sporadic ascendants who may have died from other causes before the onset of ALS. Shortly after the discovery of TDP43 mutations causing familial ALS mutations in fused in sarcomatranslocated in liposarcoma FUSTLS another RNA binding protein were identified as causing about 4 of familial ALS and rare sporadic ALS cases.

Rethinking Als The Fus About Tdp 43 Cell
This mutation is associated with FTD and TDP-43 inclusions.
Sporadic als mutation. A 228delC frameshift mutation that truncated the last 386 amino acids of the protein was found in a 60-year-old sporadic ALS patient but was not observed in control samples 44. Familial ALS is inherited as opposed to a developed mutation and is carried in families and right now there are I think four different genes that have been. The recent finding of a mutation in the VAMPsynaptobrevin-associated membrane protein B VAPB gene as the.
Most ALS cases are sporadic with approximately 510 being familial. PRPH mutations have been identified in two sporadic ALS patients. Usually Sporadic SQSTM1 Mutations Some mutations only in ALS or FTLD ALS.
Mutations of the same genes are also found in a significant proportion of sporadic ALS cases. Aims and background. The DNAJC7 pQ134Rfs6 mutation was identified in one of the 254 unexplained sporadic ALS patients 04.
Of note FUS mutation frequency is especially high in sporadic early onset ALS patients because of de novo mutations. Also occur in controls. 1 To date mutations in more than 120 genes have been shown to cause or increase the risk of ALS alsodacuk with mutations in about 20 genes being linked to monogenic forms of ALS.
According to the ALS Therapy Development Institute More than 30 genes have been identified with mutations associated with ALS Advances in genomic sequencingand the rapidity with which such sequencing can be done in research laboratoriesis behind the progress in discovering the causes of the disease. Both men and women are equally likely to inherit the genetic mutation. Three different heterozygous missense mutations in exon 6 of TARDBP pM337V pN345K and pI383V were identified in the analysis of 92 familial ALS patients 33 while no mutations were detected in 24 patients with sporadic ALS or 180 patients with other TDP-43-positive neurodegenerative diseases.
Mutations in several genes can cause familial ALS and contribute to the development of sporadic ALS. We screened the TARDBP gene in 285 French sporadic ALS patients to assess the frequency of TARDBP mutations in ALS. Mutations in the TARDBP gene which encodes the TAR DNA binding protein TDP-43 have been described in individuals with familial and sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis ALS.
1 These findings suggest that DNAJC7 mutations are not a common cause of ALS. The phenotype of the patients carrying this mutation seems to be able to be specified. Knowing the underlying cause of the disease in familial cases does not currently result in better or different treatment options compared to sporadic cases though therapeutic strategies targeting specific forms of gene mutation associated ALS are currently in research and clinical drug development pipelines.
People with FALS often start showing symptoms at earlier ages than in sporadic ALS. The major protein component of these accumulations in familial cases with SOD1 mutations 32 as well as in mutant SOD1 mouse models 8 48 70 is SOD1 itself. Like TDP43 FUSTLS is a nuclear protein with many RNA regulation and processing functions.
A common feature of both inherited and sporadic ALS is the accumulation of abnormal proteinaceous inclusions in motor neurons and glial cells. On the contrary there are no convincing data concerning a major contribution of de novo mutations in additional genes in ALS pathogenesis 16 although this has been claimed by initial studies 12 37. It is estimated that 4060 of individuals with familial ALS have an identified genetic mutation.
In sporadic cases SALS de novo mutations in the Sod1 gene have occasionally been observed. Amanda If they dont have familial ALS I dont think most PALS get a genetic test to see if they have a genetic mutation that might predispose them to ALS and they are just considered sporadic. In another recent study DNAJC7 protein-truncating variants were identified in 8 out of 5095 016 ALS patients.
Mutations in the CuZn superoxide dismutase Sod1 gene have been reported to cause adult-onset autosomal dominant Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis FALS. Superoxide dismutase 1 SOD1 mutations are the second most common cause of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis ALS explaining approximately 1220 of familial and 12 of sporadic ALS. This means a parent who has a genetic change or mutation that causes ALS has a 50 chance of passing that mutation to each of his or her children.
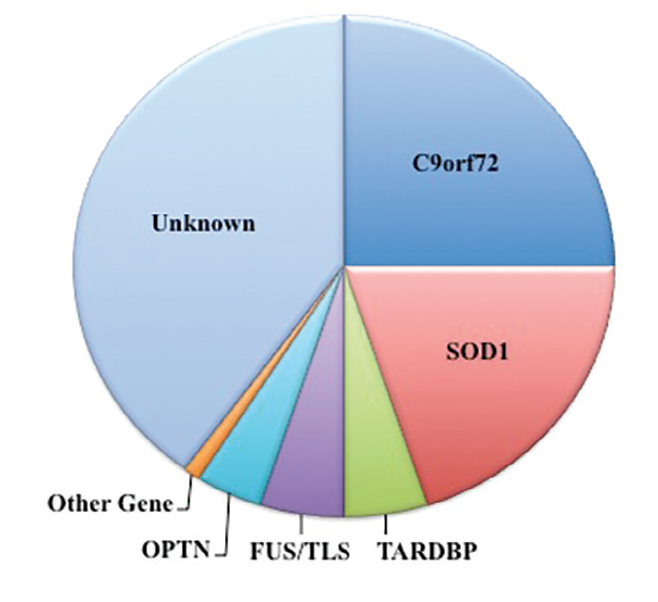
FALS is most often autosomal dominant. Variants more in ALS or FTLD Present in 2 to 3 of familial. Mutations in the C9orf72 gene account for 30 to 40 percent of familial ALS in the United States and Europe.
The most common gene mutation associated with familial and some sporadic ALS cases is hexanucleotide GGGGCC repeat expansion in a noncoding region of C9ORF72 gene on 9p21.

The Age Of Disease Onset In Fals Patients With Fus Mutations A Download Scientific Diagram
Genetic Causes Of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Als A Prevalence Download Scientific Diagram

Sod1 In Neurotoxicity And Its Controversial Roles In Sod1 Mutation Negative Als Semantic Scholar